
Muziku V Formate Dsf Dsd Torrent
At an absolute minimum, this server should have a PIII-compatible 600 MHz or newer processor with 1GB RAM. Symantec ghost 32 free download. GSS Server: We recommend running the GSS Server components on a modern, dedicated server with a 1 GHz or faster processor with 1 GB or more of RAM. GSS Agent (DAgent, and ADLAgent): GSS Agents require network connectivity and at least 10 MB disk space. Other system requirements are the same as the host operating system.
Download VA - SACD Compilation [SACD DSF] torrent or any other torrent from the Audio FLAC. Direct download via magnet link. Details for this torrent. VA - SACD Compilation [SACD DSF] Type: Audio > FLAC. All the stuff I've posted is DSD 64 bit. DSD 128 bit is coming in 2 years. CYBERGODSIG at 2014-08-26 20:48 CET: I have no.
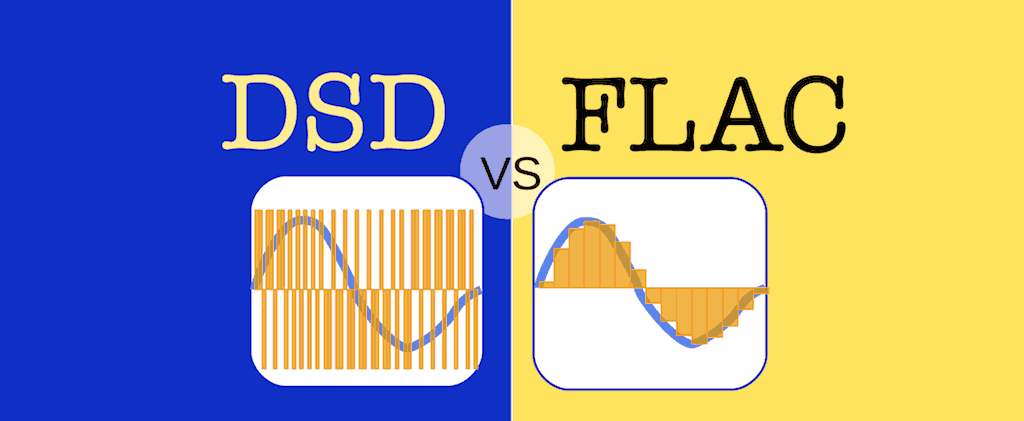
The DSD format seems to be back in fashion again. Most new digital products boast DSD compatibility, and the music catalogue is now big enough to command respect, especially if you’re into jazz and classical. But what is it? And how is it different from the digital signals used in CDs and every other format? Let us explain. PCM explained Digital signals take the form of two states that can be represented by 0 and 1, but this information needs to be arranged in a specific way to be of any use.
In just about every case the system to organise the digits is known as PCM (Pulse Code Modulation). Let’s have a quick recap of how PCM works before we continue. With PCM, the original analogue music waveform is described in two parts.
The first is its amplitude (size). In CD this is represented by 16-bits of digital data, which gives us the ability to define 65,536 different signal levels.
The original music waveform has to be measured at regular intervals in order for it to be represented properly. The measurement is done 44,100 times a second.
While that looks like an arbitrarily large number, it’s chosen quite carefully to ensure that the full frequency range of human hearing (20Hz to 20kHz) is covered. DSD and SACD DSD (Direct Stream Digital) takes a different approach. Back in the mid-1990s, it was originally conceived as a way of archiving old analogue recordings. It was designed to be a simpler, more space efficient way of storing digital music data than PCM. Importantly, DSD was also designed to be easy to convert to PCM files with sampling rates based on multiples of 44.1kHz. Around the same time, and were developing a replacement for CD, something that ultimately became the SACD disc.
DSD seemed an ideal system to build the new format around, particularly as it has great copy protection. The main attraction of DSD is its simplicity and, with that, cheapness of implementation. It needs less processing than PCM and can use simpler, far less expensive s. How does DSD work?
DSD uses a single bit of information, and all this information tells us is whether the current sample of the analogue waveform is higher or lower than in the previous one. Compared with the over 65,000 different values 16-bit PCM has, the two values (0 if the new sample if the signal is lower or 1 if it’s higher) of DSD appear mighty limiting. That resolution shortfall is made up by the very high sampling rate of over 2.8 million times a second – that’s 64 times the speed of CD.
Standard DSD is sometimes called DSD64 for this reason, with double and quadruple speed versions called DSD128 and DSD256 respectively. There's even a DSD512 spec, though we've never heard any material encoded in it.
Items that were attained significantly earlier, later, and around the same age by the Metro-Manila children compared to the other groups were determined. Denver ii developmental screening test form. The Metro-Manila children performed similarly on the test as the Tokyo and Okinawa children on the gross motor, fine motor-adaptive, language, and personal-social sectors of the test.
Standard DSD recordings are still relatively rare compared with the PCM alternatives, and those higher speed versions are extremely niche. DSD fans claim the format is as close to analogue as digital gets. If you could look at a DSD digital stream, it’s possible to draw the analogue waveform simply by looking at the density of 0s and 1s. The more 0s there are, the lower the waveform goes, and it’s the opposite for ones.
Where there is a balance of the two values, we’re at, or close to, the zero signal point. What are the downsides to DSD? Astell & Kern's AK70 mkII converts DSD files to PCM for playback That all looks good, but there are also issues with DSD. It’s not very practical to manipulate a DSD recording. All the things that are required post-recording such as equalisation, editing, dynamic range control and adding reverb usually involve the DSD stream being converted to PCM to do the processing and then switched back. That’s hardly a pure way of doing things, right? Just about every studio recording made with DSD goes through this process.